Understanding the Parts of the Body in English
Learning the Parts of the Body in English is essential for English language learners as it helps to communicate about health, emotions, and physical activities. Let’s break down the main parts of the human body, starting from the head down to the toes.
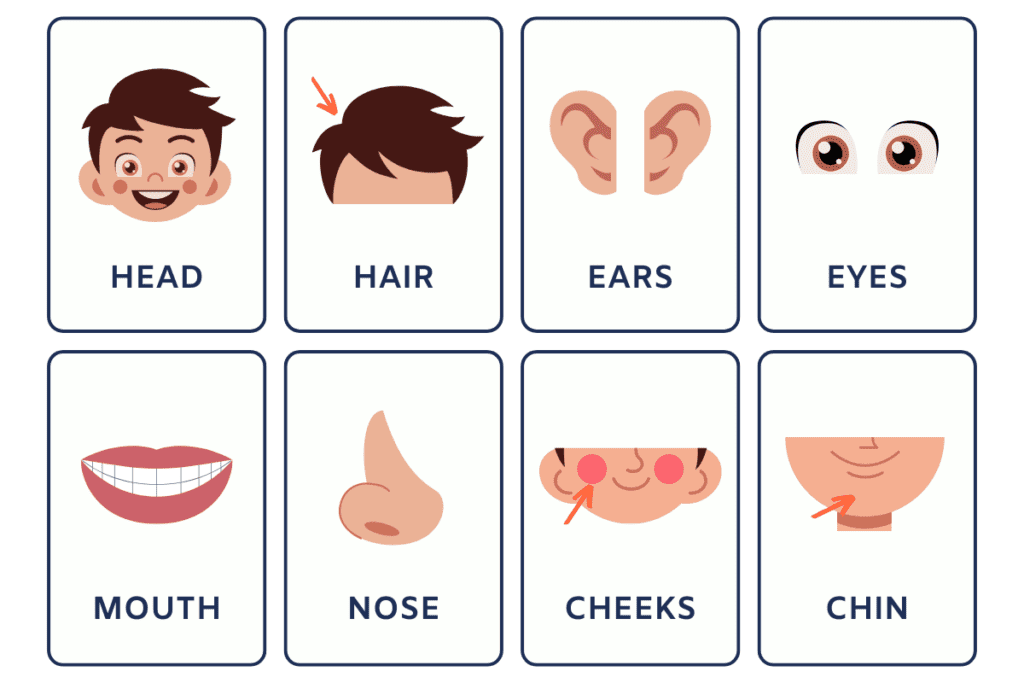
the Parts of the Body in English: Vocabulary
The Head:
The head is the uppermost part of the body, containing several vital organs. Let’s break down the key components of the head:
Eyes: Used for seeing, the eyes are one of the most important senses.
- Example sentence: “My eyes are tired from staring at the computer screen all day.”
Ears: Responsible for hearing, the ears play a crucial role in our daily lives.
- Example sentence: “I need to clean my ears because they feel blocked.”
Nose: The nose is used for smelling and breathing.
- Example sentence: “I have a cold, and my nose is stuffy.”
Mouth: The mouth is used for eating, speaking, and expressing emotions.
- Example sentence: “I need to brush my teeth to keep my mouth clean.”
Forehead: The area above the eyes, and the forehead can be used to express emotions.
- Example sentence: “I have a headache, and my forehead is hurting.”
Cheeks: The round parts of the face, and cheeks can be used to describe emotions.
- Example sentence: “Her cheeks turned red when she was embarrassed.”
Chin: The lower part of the face, the chin can be used to describe someone’s appearance.
- Example sentence: “He has a strong chin, which makes him look confident.”
Hair: Growing on top of the head, hair can be styled in various ways.
- Example sentence: “I need to wash my hair because it’s dirty.”
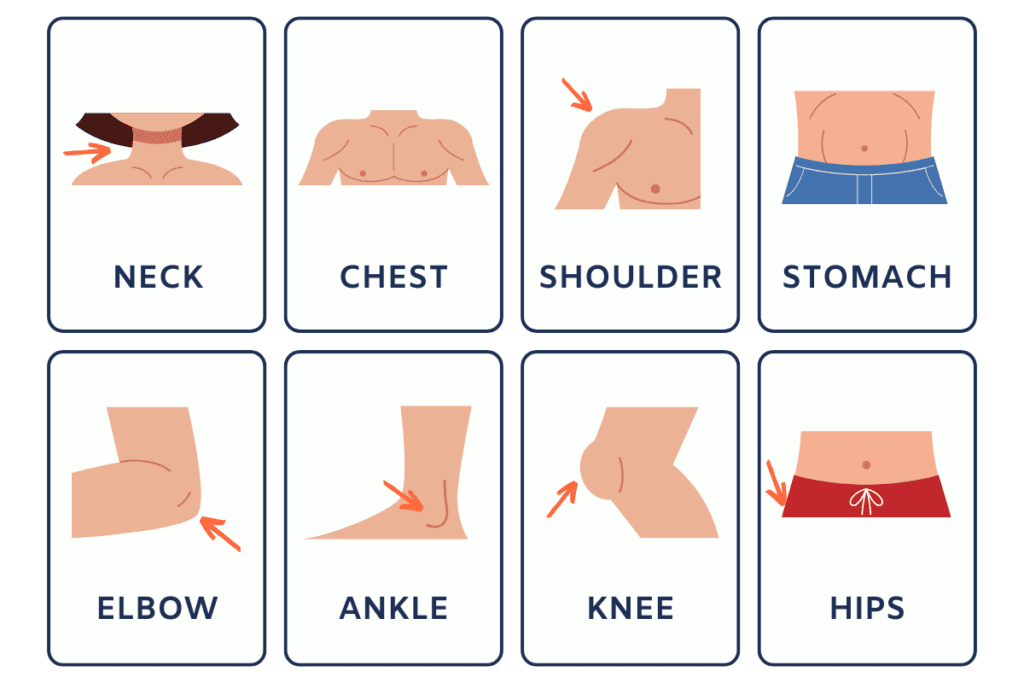
The Torso:
The torso, also known as the trunk, is the central part of the body. It contains vital organs and is divided into two main sections: the chest and the abdomen.
Chest: The upper part of the torso, the chest contains the heart and lungs.
- Example sentence: “I have a chest infection, and I need to see a doctor.”
Abdomen: The lower part of the torso, the abdomen contains the stomach and other digestive organs.
- Example sentence: “I have a stomachache, and I need to take some medicine.”
Shoulders: Connect the arms to the torso.
- Example: “He shrugged his shoulders.”
Back: The rear part of the torso, the back provides support and protection for the body.
- Example sentence: “I have a backache, and I need to stretch my muscles.”
Waist: The narrow part of the torso, the waist is located between the ribs and hips.
- Example sentence: “I need to lose weight around my waist.”
The Limbs:
The limbs are the extremities of the body, consisting of the arms and legs.
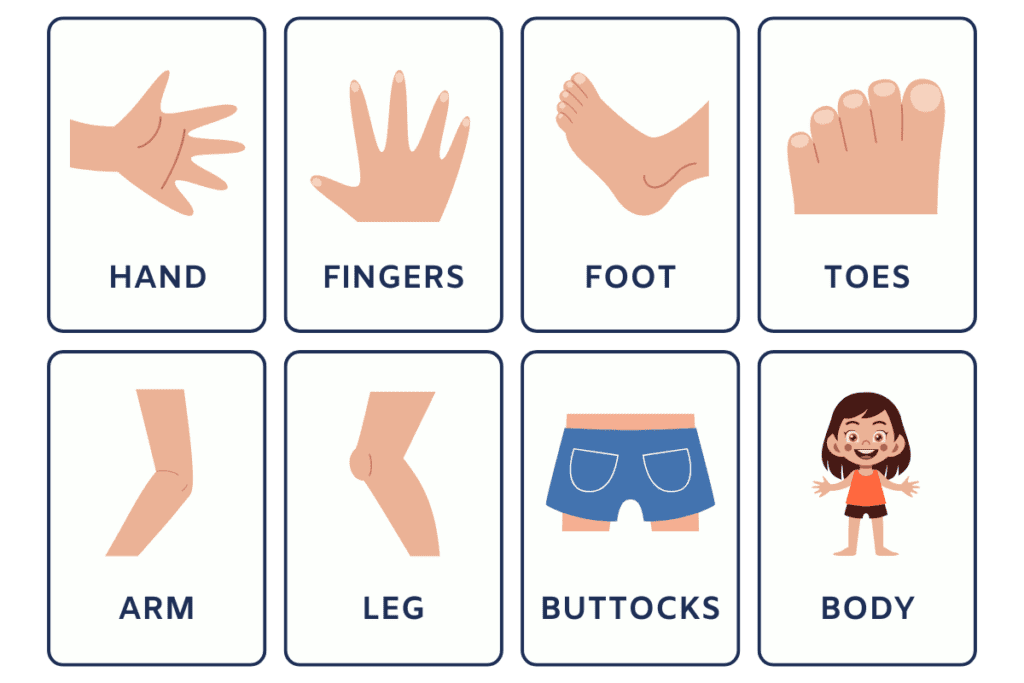
Upper Limbs (Arms): The upper limbs, and arms are used for movement and grasping objects.
Shoulder: The joint that connects the arm to the torso.
- Example sentence: “I have a shoulder injury, and I need to rest my arm.”
Elbow: The joint that connects the upper arm to the forearm.
- Example sentence: “I bumped my elbow, and it hurts.”
Wrist: The joint that connects the forearm to the hand.
- Example sentence: “I have a wristwatch that I wear every day.”
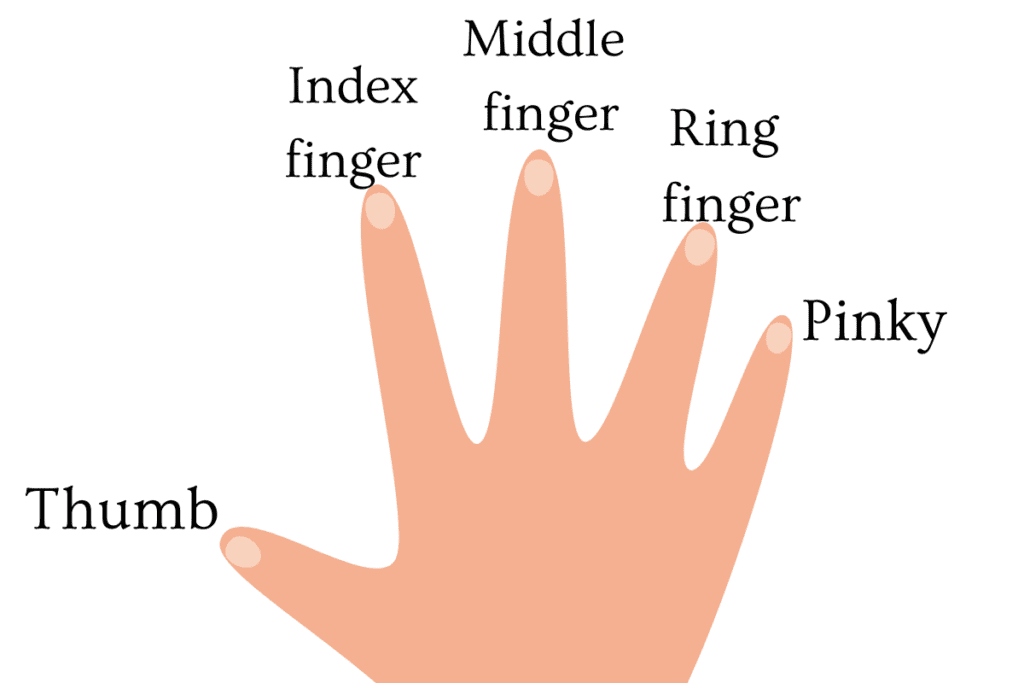
Hand: The end of the arm, used for grasping and manipulating objects.
- Fingers: The individual digits of the hand.
- Thumb: The first finger, used for grasping and opposition.
- Example sentence: “I hurt my thumb, and it’s hard to type.”
- Index finger: The second finger, is used for pointing and manipulation.
- Example sentence: “I use my index finger to click the mouse.”
- Middle finger: The third finger, is used for balance and support.
- Example sentence: “I wear a ring on my middle finger.”
- Ring finger: The fourth finger, is used for wearing rings and other jewelry.
- Example sentence: “I wear my wedding ring on my ring finger.”
- Pinky: The fifth finger, is used for balance and support.
- Example sentence: “I have a pinky ring that I wear every day.”
Lower Limbs (Legs): The lower limbs, and legs are used for movement and support.
Hip: The joint that connects the leg to the torso.
- Example sentence: “I have a hip injury, and I need to see a doctor.”
Knee: The joint that connects the thigh to the calf.
- Example sentence: “I have a knee injury, and I need to wear a brace.”
Ankle: The joint that connects the calf to the foot.
- Example sentence: “I twisted my ankle, and it hurts to walk.”
- Foot: The end of the leg, used for balance and movement.
- Toes: The individual digits of the foot.
- Big toe: The first toe, used for balance and support.
- Example sentence: “I hurt my big toe, and it’s hard to walk.”
- Other toes: The remaining toes, used for balance and support.
- Example sentence: “I have to trim my toenails because they’re too long.”
- Toes: The individual digits of the foot.
The Internal Parts of the Body In English
Understanding the internal parts of the body is crucial for English learners, as it allows for meaningful conversations about health, wellness, and biology. In this section, we’ll identify some key internal organs and their functions, providing you with essential vocabulary.
1. Heart: The heart is a vital organ located in the chest. It pumps blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues while removing carbon dioxide and waste products.
2. Lungs: The lungs are two essential organs located in the chest, responsible for breathing. They take in oxygen from the air and release carbon dioxide, enabling us to breathe.
3. Stomach: The stomach is part of the digestive system, located in the abdomen. It breaks down food using acids and enzymes. After the stomach, the food moves into the small intestine.
4. Small and Large Intestines: The small intestine absorbs nutrients from food, while the large intestine absorbs water and processes waste, forming stool.
5. Liver: The liver is the largest internal organ and has various functions, including detoxifying blood, producing bile for digestion, and storing nutrients.
6. Kidneys: The kidneys filter waste from the blood and produce urine, balancing fluids in the body. They are essential for maintaining overall health.
7. Brain: The brain, protected by the skull, coordinates body functions, processes information, and controls thoughts and emotions, making it a crucial part of the nervous system.
8. Spleen: The spleen helps filter blood and is involved in immune responses. It’s located in the upper left part of the abdomen and plays a role in fighting infections.
9. Pancreas: Located behind the stomach, the pancreas produces digestive enzymes and regulates blood sugar by releasing insulin.
Using Body Vocabulary in Sentences
Understanding body vocabulary is essential, but using it in sentences makes it even more effective. Practice forming sentences with the words learned. For instance:
- “I exercise to keep my heart strong.”
- “She is covering her ears because the music is too loud.”
- “He hurt his knee while playing football.”
Idioms with Parts of the Body In English
In addition to vocabulary, English learners can also explore idiomatic expressions related to the human body. These idioms help make your language more engaging and natural, and using them can improve your communication skills. Let’s explore some common body-part idioms, categorized into parts of the body for easy reference.
1. Head and Brain:
- Head over heels: completely in love (e.g., “They’re head over heels in love.”)
- Head in the sand: ignoring problems or difficult situations (e.g., “She’s trying to bury her head in the sand.”)
- Bright as a button: clever or intelligent (e.g., “He’s been a professor at the university for years and is still as bright as a button.”)
- Out of one’s mind: crazy or irrational (e.g., “He’s out of his mind if he thinks he can finish this project in a day.”)
- Brainstorming: generating new ideas through a group discussion (e.g., “We had a brainstorming session before writing the proposal.”)
2. Eyes:
- See eye to eye: to have the same opinion or point of view (e.g., “We see eye to eye on the new policy.”)
- Keep an eye on: to watch or observe someone or something (e.g., “Keep an eye on your wallet when you’re in public.”)
- Give someone the eye: to flirt with someone by looking at them in a certain way (e.g., “He gave her the eye, but she ignored him.”)
3. Heart and Love:
- Break one’s heart: to make someone very sad (e.g., “He broke his heart when they broke up.”)
- Have a heart of gold: to be kind and generous (e.g., “She’s always been a kind person, and everyone says she has a heart of gold.”)
- Fall head over heels in love: to be deeply in love at first sight (e.g., “They fell head over heels in love when they met.”)
4. Body Movement and Actions:
- Get under someone’s skin: to annoy or irk someone (e.g., “His constant noise is getting under my skin.”)
- Get a leg up: to gain an advantage or have an edge (e.g., “Having a good education got her a leg up in the job market.”)
5. Additional Expressions:
- Have a bad blood: to have a strong dislike or grudge (e.g., “He and his sister have bad blood.”)
- Bite one’s tongue: to remain silent and not say what someone is thinking (e.g., “I have to bite my tongue when I see that movie, it annoys me.”)
- Take a deep breath: to relax and calm down (e.g., “Take a deep breath and try again.”)
Incorporating these idioms into your language will help you express yourself more vividly and naturally in English. Practice using them in context to improve your communication skills!
Parts of the Body In English: Conclusion:
In conclusion, learning the parts of the body in English is essential for effective communication. By mastering these terms, you’ll be able to describe your physical experiences, discuss health issues, and engage in everyday conversations with confidence.